Top Energy Conservation Solutions Homebuyers Seek
Solar Energy Systems
The heading “Solar Energy Systems” refers to the installation of photovoltaic (PV) panels on a residential property to harness sunlight and convert it into electricity. Top Energy Conservation Solutions Homebuyers Seek. Here’s an expanded explanation:
Solar Energy Systems:
In the context of energy conservation solutions sought by homebuyers, “Solar Energy Systems” typically involves the installation of solar panels on rooftops or other suitable locations on the property. These systems capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, which directly contributes to reducing reliance on grid-supplied electricity.
Key Points:
Renewable Energy Source: Solar energy is renewable and abundant, providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Reduced Energy Bills: By generating electricity onsite, homeowners can potentially lower their energy bills, especially in regions with abundant sunlight.
Environmental Benefits: Solar energy systems reduce carbon footprint and greenhouse gas emissions associated with traditional electricity generation.
Long-Term Investment: Despite initial installation costs, solar panels can offer long-term savings and increase property value.
Energy Independence: Homeowners gain a degree of energy independence and resilience against fluctuating energy prices.
Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives such as tax credits or rebates to encourage the adoption of solar energy, making it a financially viable option for homeowners.
In summary, “Solar Energy Systems” represent a significant energy conservation solution sought by homebuyers looking to reduce their environmental impact, save on energy costs, and increase the sustainability and value of their homes.
Energy-Efficient Appliances

The heading “Energy-Efficient Appliances” refers to household appliances that are designed to consume less energy compared to standard models while providing the same level of functionality and performance. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Energy-Efficient Appliances:
Energy-efficient appliances are designed with advanced technologies and engineering that enable them to operate using less electricity, natural gas, or water without compromising their functionality. These appliances contribute significantly to reducing overall energy consumption in households, thereby lowering utility bills and environmental impact.
Key Points:
Energy Savings: Energy-efficient appliances consume less electricity or other resources (such as water for washing machines and dishwashers) during operation, leading to reduced energy bills over time.
Environmental Impact: By consuming less energy, these appliances help decrease greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants associated with electricity generation.
Government Standards and Labels: Many countries have established energy efficiency standards and labels (e.g., Energy Star in the United States) to help consumers identify and choose energy-efficient appliances.
Range of Appliances: Energy-efficient appliances span various categories including refrigerators, washing machines, dishwashers, air conditioners, water heaters, and more.
Technological Advancements: Advances in technology, such as improved insulation, compressor technology, and sensor-based operation, contribute to the efficiency of these appliances.
Long-Term Savings: While energy-efficient appliances may have a higher upfront cost compared to standard models, the potential savings on energy bills and reduced maintenance costs often make them a cost-effective choice in the long run.
In summary, “Energy-Efficient Appliances” play a crucial role in modern homes by not only reducing energy consumption and utility costs but also promoting environmental sustainability through lower resource use and emissions. They are a key consideration for homebuyers looking to create an energy-efficient and eco-friendly living environment.
Smart Home Technology Integration
The heading “Smart Home Technology Integration” refers to the incorporation of advanced technological systems and devices into residential properties to enhance convenience, efficiency, security, and energy conservation. Here’s a comprehensive explanation:
Smart Home Technology Integration:
Smart home technology integration involves the installation and connectivity of various devices, systems, and appliances within a home environment that can be controlled and automated remotely or through a centralized system. These technologies are designed to streamline operations, improve energy efficiency, and provide homeowners with greater control over their living spaces.
Key Points:
Connected Devices: Smart home integration includes devices such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, security cameras, door locks, appliances, and entertainment systems that can be interconnected and controlled via a smartphone, tablet, or voice commands.
Energy Efficiency: Smart home technologies contribute to energy conservation by allowing users to monitor and optimize energy use. For example, smart thermostats can adjust heating and cooling based on occupancy and weather conditions, reducing energy waste.
Convenience and Automation: Automation features enable tasks such as turning off lights, adjusting temperatures, or activating security systems to occur automatically based on preset schedules or environmental conditions.
Enhanced Security: Integration of smart security systems provides real-time monitoring and alerts for intrusions, smoke detection, or other emergencies, enhancing home safety.
Remote Access: Homeowners can remotely control and monitor their smart devices from anywhere with an internet connection, offering peace of mind and flexibility.
Personalization: Smart home technology allows for personalized settings and preferences, such as customized lighting scenes, music playlists, or room temperatures, tailored to individual lifestyles.
Data Insights: Some smart systems collect data on energy usage and habits, providing insights that help optimize resource consumption and improve efficiency over time.
Compatibility and Expandability: Many smart home devices are designed to be compatible with each other and can be expanded or upgraded as technology advances, ensuring long-term usability and functionality.
In summary, “Smart Home Technology Integration” represents a modern approach to home management that enhances convenience, security, and energy efficiency through interconnected devices and systems. It is a compelling option for homebuyers seeking to leverage technology to create a more efficient, comfortable, and responsive living environment.
High-Efficiency HAC Systems
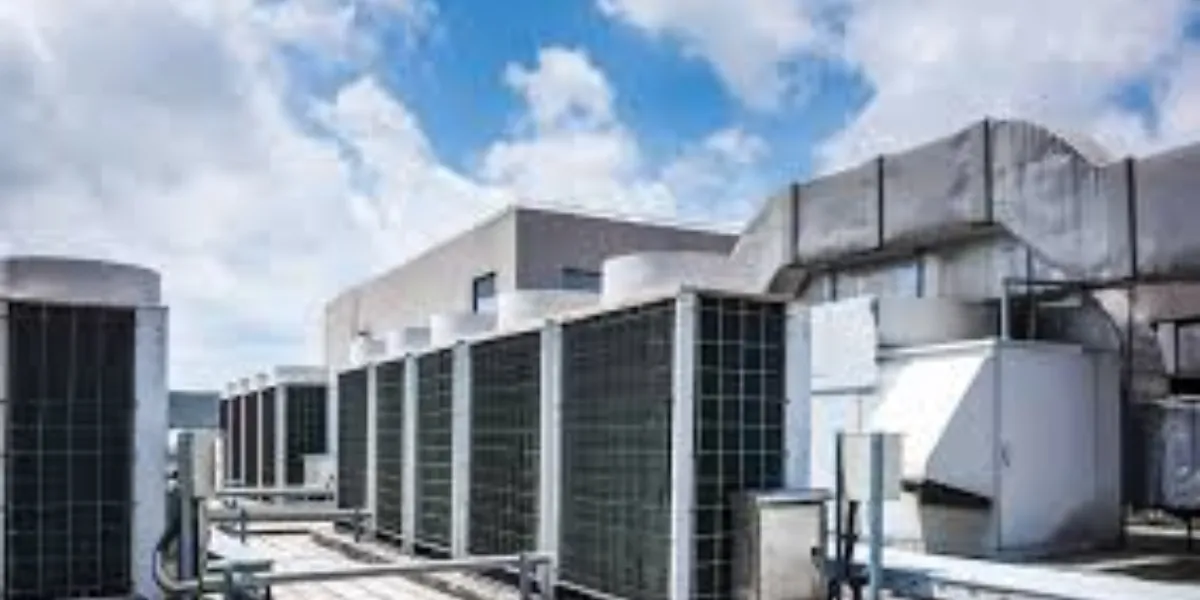

The heading “High-Efficiency HVAC Systems” refers to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems designed to optimize energy use and performance while maintaining or improving indoor comfort levels. Here’s a detailed explanation:
High-Efficiency HVAC Systems:
High-efficiency HVAC systems are advanced heating and cooling units that utilize innovative technologies to reduce energy consumption compared to traditional systems. These systems are designed to provide effective climate control while minimizing operating costs and environmental impact.
Key Points:
Energy Savings: High-efficiency HVAC systems consume less energy to achieve the same heating and cooling output as standard systems. This results in lower utility bills and reduced overall energy consumption.
Advanced Technology: They incorporate features such as variable-speed motors, advanced heat exchangers, and improved insulation to maximize efficiency and performance.
Environmentally Friendly: By reducing energy consumption, high-efficiency HVAC systems help lower greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to environmental sustainability.
Enhanced Comfort: These systems often provide more precise temperature and humidity control, resulting in improved comfort levels and indoor air quality.
Quiet Operation: Many high-efficiency units are designed to operate more quietly than standard HVAC systems, enhancing the overall indoor environment.
Long-Term Savings: Despite potentially higher initial costs, the energy savings and reduced maintenance expenses over the lifespan of high-efficiency HVAC systems often make them a cost-effective investment.
Government Incentives: Many governments offer incentives, such as tax credits or rebates, to encourage the installation of high-efficiency HVAC systems, making them more financially attractive to homeowners.
Integration with Smart Home Technology: High-efficiency HVAC systems can often be integrated with smart home technology, allowing for remote monitoring, scheduling, and energy management.
In summary, “High-Efficiency HVAC Systems” represent a significant advancement in residential climate control technology, offering homeowners the opportunity to achieve superior comfort, lower energy costs, and reduced environmental impact. They are a key consideration for homebuyers seeking energy-efficient solutions that enhance both their quality of life and their home’s value.
Insulation and Weatherization
The heading “Insulation and Weatherization” refers to the methods and materials used to improve the thermal efficiency of a home by reducing heat transfer and air leakage. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Insulation and Weatherization:
Insulation and weatherization are essential components of energy conservation in homes. They involve enhancing the building envelope—walls, floors, ceilings, windows, and doors—to minimize heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. These measures not only improve energy efficiency but also enhance comfort levels and reduce utility costs.
Key Points:
Types of Insulation: Various insulation materials, such as fiberglass, cellulose, foam, and mineral wool, are used to create a thermal barrier within walls, attics, and floors. Each material has its own thermal resistance (R-value) which indicates its effectiveness in resisting heat transfer.
Air Sealing: Weatherization includes sealing gaps, cracks, and joints in the building envelope to prevent air leakage. This can be done with caulking, weatherstripping, and applying spray foam insulation around windows, doors, and penetrations.
Benefits of Insulation:
Energy Savings: Proper insulation reduces the need for heating and cooling, resulting in lower energy bills.
Comfort: Insulation helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures and reduces drafts, enhancing comfort throughout the home.
Noise Reduction: Insulation can also provide soundproofing benefits by dampening noise from outside or between rooms.
Weatherization Benefits:
Energy Efficiency: Weatherization measures complement insulation by reducing air leakage, thereby optimizing the effectiveness of HVAC systems.
Moisture Control: Proper sealing and insulation can help prevent moisture condensation and related issues like mold growth.
Durability: Enhancing the building envelope through weatherization can improve the durability and lifespan of the home’s structural components.
Considerations for Homebuyers: When purchasing a home, buyers often prioritize properties with adequate insulation and weatherization as these features contribute to lower utility costs, improved indoor comfort, and a more sustainable living environment.
Environmental Impact: Improving insulation and weatherization reduces the home’s carbon footprint by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with heating and cooling.
In summary, “Insulation and Weatherization” are critical elements of energy-efficient home design and renovation. They play a significant role in reducing energy consumption, improving comfort, and enhancing the overall performance and sustainability of residential buildings.
Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors
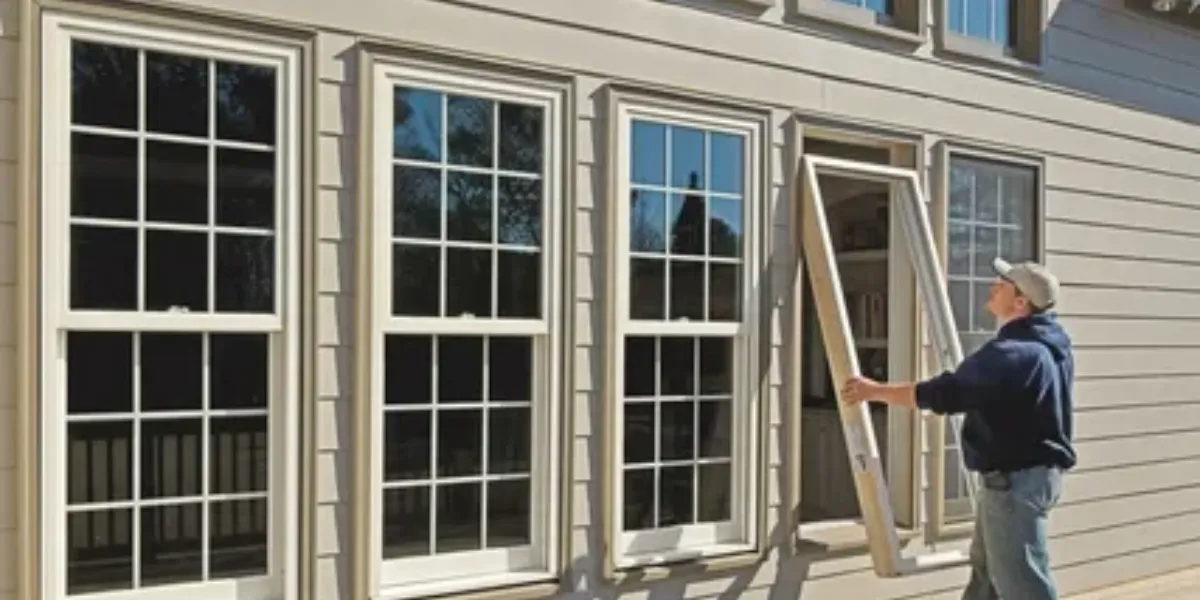

The heading “Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors” refers to the installation of specially designed windows and doors that minimize heat loss or gain, improve insulation, and enhance overall energy efficiency within a home. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors:
Energy-efficient windows and doors are designed to reduce energy consumption by improving thermal insulation, minimizing air leakage, and often incorporating advanced glazing technologies. These features help maintain more consistent indoor temperatures, enhance comfort, and reduce heating and cooling costs.
Key Points:
Insulated Glazing: Energy-efficient windows typically feature double or triple-pane glass with insulating gas fills (such as argon or krypton) between the panes. This construction reduces heat transfer through the windows, improving thermal performance.
Low-E Coatings: Many energy-efficient windows have Low-E (low-emissivity) coatings applied to the glass surfaces. These coatings reflect infrared heat while allowing visible light to pass through, reducing heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter.
Frame Materials: Frames of energy-efficient windows and doors are often made from materials that offer better thermal resistance, such as vinyl, fiberglass, or insulated wood frames. These materials reduce the transfer of heat and cold between the interior and exterior of the home.
Air Leakage Prevention: Proper installation and sealing techniques ensure that energy-efficient windows and doors minimize air leakage, preventing drafts and improving overall comfort.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors:
Energy Savings: By reducing the need for heating and cooling, energy-efficient windows and doors help lower utility bills.
Improved Comfort: Enhanced insulation and reduced air leakage contribute to more consistent indoor temperatures and reduced drafts.
UV Protection: Some energy-efficient windows also provide protection against UV radiation, which can help prevent fading of furniture, flooring, and interior decor.
Environmental Impact: Energy-efficient windows and doors contribute to reducing a home’s carbon footprint by decreasing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with heating and cooling.
Considerations for Homebuyers: Homebuyers often prioritize properties with energy-efficient windows and doors due to their potential for long-term cost savings, improved comfort, and environmental benefits.
In summary, “Energy-Efficient Windows and Doors” are integral components of sustainable home design, offering homeowners enhanced comfort, reduced energy bills, and a smaller environmental footprint. They represent a significant investment in improving the overall efficiency and performance of residential buildings.
LED Lighting Solutions
The heading “LED Lighting Solutions” refers to the use of Light Emitting Diode (LED) technology for illumination purposes in residential settings. Here’s a detailed explanation:
LED Lighting Solutions:
LED lighting solutions involve the use of LED bulbs and fixtures throughout a home to provide efficient and effective lighting. LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They offer several advantages over traditional incandescent and fluorescent lighting technologies, making them increasingly popular in residential applications.
Key Points:
Energy Efficiency: LED bulbs are highly energy-efficient, consuming significantly less electricity than incandescent and fluorescent bulbs for the same amount of light output. This efficiency translates to lower energy bills and reduced overall energy consumption in homes.
Long Lifespan: LEDs have a much longer lifespan compared to traditional bulbs. They can last tens of thousands of hours, which means less frequent replacement and lower maintenance costs for homeowners.
Durability and Reliability: LEDs are solid-state devices that are resistant to shock, vibrations, and external impacts, making them more durable and reliable than fragile incandescent and fluorescent bulbs.
Instantaneous Lighting: LED bulbs reach full brightness instantly upon being switched on, unlike some other types of lighting that may require warm-up time.
Compact and Versatile: LED technology allows for compact designs and various form factors, enabling creative and efficient lighting solutions for different areas of the home, including recessed lighting, track lighting, and decorative fixtures.
Color Options: LEDs are available in a wide range of color temperatures, from warm white to cool daylight, providing flexibility to homeowners in achieving desired ambiance and lighting effects.
Dimmable Options: Many LED bulbs and fixtures are dimmable, allowing users to adjust the brightness level according to their needs and preferences.
Environmental Benefits: LED lighting contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation. They also contain no mercury or other hazardous substances, unlike fluorescent bulbs.
Integration with Smart Home Systems: LED lighting can be integrated with smart home systems for remote control, scheduling, and automation, enhancing convenience and energy management.
In summary, “LED Lighting Solutions” represent a significant advancement in residential lighting technology, offering homeowners energy savings, durability, versatility, and environmental benefits. They are a preferred choice for homebuyers looking to improve energy efficiency and lighting quality within their homes.
Water Conservation Features
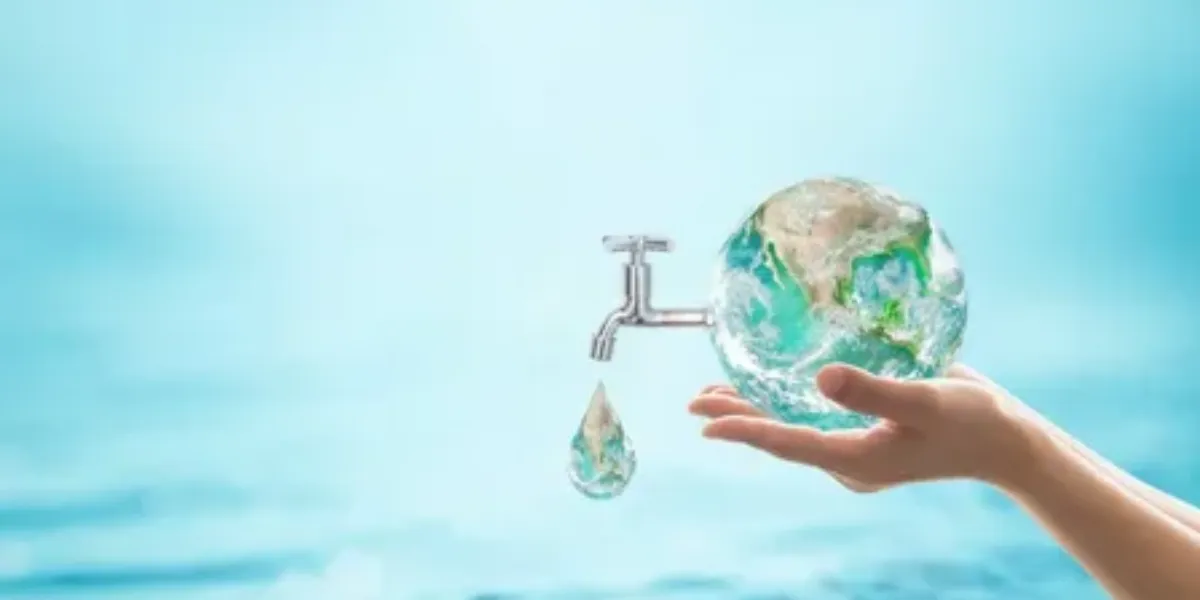

The heading “Water Conservation Features” refers to various technologies, practices, and fixtures implemented in residential properties to minimize water usage and promote efficient water management. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Water Conservation Features:
Water conservation features encompass a range of strategies and products designed to reduce water consumption in homes. These features aim to optimize water usage, mitigate water waste, and promote sustainability in residential water management.
Key Points:
Low-Flow Fixtures: Installation of low-flow fixtures such as faucets, showerheads, and toilets that are designed to restrict water flow without compromising performance. These fixtures can significantly reduce water usage compared to conventional counterparts.
Water-Efficient Appliances: Selection of water-efficient appliances like dishwashers and washing machines that use less water per cycle while maintaining effective cleaning performance. Energy Star-rated appliances often include water-saving features.
Smart Irrigation Systems: Integration of smart irrigation controllers and drip irrigation systems in outdoor landscapes to deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. These systems can be programmed based on weather conditions and soil moisture levels.
Greywater Systems: Utilization of greywater systems to capture and reuse water from sinks, showers, and laundry for purposes such as landscape irrigation or toilet flushing, reducing reliance on fresh water sources.
Rainwater Harvesting: Implementation of rainwater harvesting systems to capture rainwater from roofs and store it for non-potable uses like irrigation, outdoor cleaning, and toilet flushing.
Leak Detection and Repair: Regular inspection and prompt repair of leaks in plumbing fixtures, pipes, and irrigation systems to prevent water wastage and ensure efficient water use.
Educational Programs: Promotion of water-saving behaviors and practices among homeowners through educational programs, incentives, and public awareness campaigns.
Water Metering and Monitoring: Installation of water meters and monitoring systems to track water usage patterns, identify inefficiencies, and encourage conservation efforts.
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to local building codes and regulations that mandate the installation of water-efficient fixtures and systems in new construction and home renovations.
Environmental Benefits: Water conservation features contribute to preserving freshwater resources, reducing energy consumption associated with water treatment and distribution, and minimizing environmental impact.
In summary, “Water Conservation Features” play a crucial role in sustainable residential design and management. They help homeowners reduce water bills, conserve valuable water resources, and contribute to environmental stewardship by promoting efficient water use practices within households.
Energy Monitoring and Management Systems
The heading “Energy Monitoring and Management Systems” refers to technologies and systems that enable homeowners to track, analyze, and optimize their energy usage throughout their residential properties. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Energy Monitoring and Management Systems:
Energy monitoring and management systems encompass a range of technologies and tools designed to monitor, measure, and control energy consumption within a home. These systems provide homeowners with insights into their energy usage patterns, enabling them to make informed decisions to improve energy efficiency and reduce utility costs.
Key Points:
Real-Time Monitoring: These systems collect and display real-time data on electricity consumption, allowing homeowners to monitor how much energy various appliances, lighting, and HVAC systems are using at any given time.
Historical Analysis: Energy management systems often store historical data, allowing homeowners to analyze trends in energy usage over days, weeks, months, or even years. This analysis helps identify inefficiencies and opportunities for energy savings.
Appliance-Level Monitoring: Some advanced systems can monitor energy usage at the individual appliance level, providing detailed insights into which appliances are the most energy-intensive and where potential savings can be made.
Remote Access and Control: Many energy management systems offer remote access via smartphone apps or web portals, allowing homeowners to monitor and control their home’s energy consumption from anywhere. This feature enables adjustments to schedules, settings, and device controls to optimize energy efficiency.
Energy Efficiency Recommendations: Some systems provide personalized recommendations for improving energy efficiency based on usage patterns and historical data. These recommendations may include adjusting thermostat settings, upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, or optimizing lighting schedules.
Integration with Smart Home Technology: Energy management systems can often integrate with other smart home devices and systems, such as smart thermostats, lighting controls, and appliances. This integration allows for automated energy-saving actions based on occupancy, weather conditions, or time of day.
Cost Savings: By identifying energy wastage and implementing efficiency improvements, homeowners can potentially reduce their energy bills and achieve long-term cost savings.
Environmental Impact: Energy monitoring and management systems contribute to environmental sustainability by promoting responsible energy consumption practices, reducing carbon footprint, and conserving natural resources.
Utility Program Participation: Some energy management systems support participation in utility demand response programs or time-of-use pricing by optimizing energy usage during peak demand periods or when electricity rates are highest.
In summary, “Energy Monitoring and Management Systems” empower homeowners with tools and insights to actively manage and optimize their energy usage. These systems are instrumental in promoting energy efficiency, reducing costs, and supporting sustainable living practices within residential environments.
Passive Design Strategies
 fWar
fWar
The heading “Passive Design Strategies” refers to architectural and design principles applied to residential buildings that harness natural resources and environmental conditions to achieve optimal comfort and energy efficiency without relying on active mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Passive Design Strategies:
Passive design strategies focus on utilizing natural elements such as sunlight, shade, airflow, and thermal mass to regulate indoor temperatures, lighting, and ventilation. These strategies aim to minimize energy consumption for heating, cooling, and lighting within homes while enhancing overall comfort and sustainability.
Key Points:
Orientation and Layout: Proper orientation of a home on its site ensures maximum exposure to beneficial sunlight during winter (to provide warmth) and minimizes exposure to harsh sunlight during summer (to reduce cooling needs). Efficient layout design can facilitate natural airflow and ventilation.
Insulation and Thermal Mass: Effective insulation in walls, floors, and roofs, combined with the use of materials with high thermal mass (such as concrete or brick), helps regulate indoor temperatures by reducing heat transfer through the building envelope.
Natural Ventilation: Strategically placed windows, operable skylights, and vents allow for cross-ventilation and airflow through the home, promoting cooling in warmer months without relying on mechanical ventilation systems.
Shading and Glazing: External shading devices such as overhangs, awnings, and vegetation help block excessive solar heat gain in summer, while high-performance glazing (such as low-E windows) minimizes heat loss in winter and reduces glare.
Daylighting: Designing with ample windows and skylights in key living spaces allows natural daylight to penetrate deep into the interior, reducing the need for artificial lighting during daylight hours and improving occupant well-being.
Passive Solar Heating: Incorporating design features like solar chimneys, trombe walls, or thermal mass in sun-exposed areas can harness solar energy to passively heat the home during colder months.
Climate-Specific Strategies: Passive design strategies are tailored to local climate conditions, considering factors such as temperature ranges, humidity levels, prevailing winds, and solar exposure patterns unique to the region.
Health and Comfort Benefits: Passive design enhances indoor environmental quality by minimizing reliance on mechanical heating and cooling, which can improve comfort, reduce noise, and promote better indoor air quality.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: By reducing reliance on active HVAC systems and artificial lighting, passive design strategies contribute to significant energy savings, lower utility costs, and reduced carbon emissions over the building’s lifespan.
In summary, “Passive Design Strategies” represent a holistic approach to sustainable building design, emphasizing the integration of natural elements and environmental considerations to create comfortable, energy-efficient homes. These strategies are increasingly valued by homeowners and architects seeking to achieve both environmental stewardship and superior living comfort in residential construction.
Click here for more visited Posts!