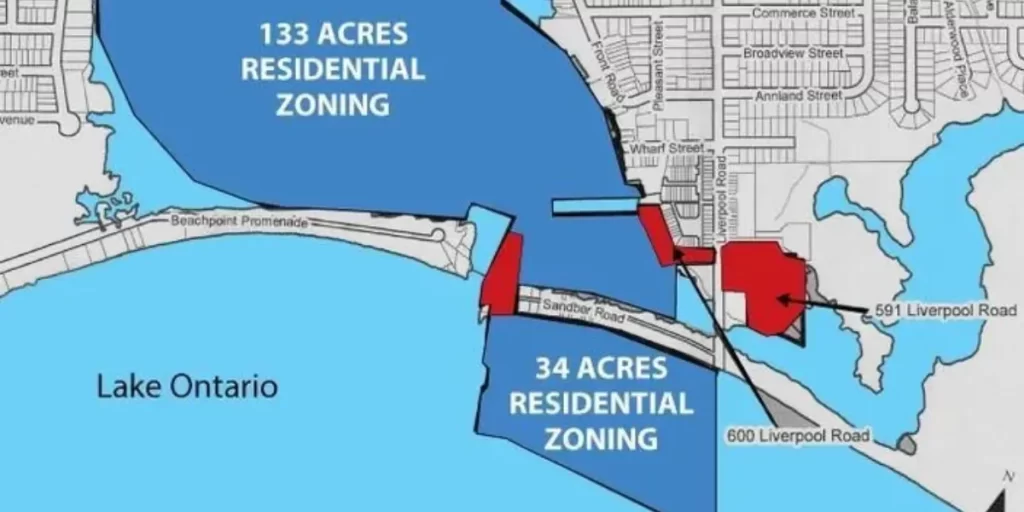
Not Even A Pandemic Can Curb Canada’s Insatiable Housing Demand

Canada’s Unstoppable Housing Demand
Canada’s housing market has long been characterized by relentless demand, and not even a global pandemic could dampen the fervor. Despite economic uncertainties and disruptions, the desire for homeownership in Canada remains undeterred . Not Even A Pandemic Can Curb Canada’s Insatiable Housing Demand . In this article, we’ll delve into the various factors propelling Canada’s insatiable housing demand, the impact of the pandemic, government interventions, and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Understanding the Factors Driving Canada’s Housing Market

Several factors contribute to the perpetual demand for housing in Canada. Urbanization, population growth, historically low-interest rates, changing consumer preferences, and the influence of foreign investors all play significant roles. These dynamics create a complex ecosystem where demand consistently outpaces supply, driving prices upward.
Impact of the Pandemic on Canada’s Housing Sector
While the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted many aspects of daily life, it surprisingly did little to curb Canada’s housing demand. Initially, there was a brief slowdown as uncertainty gripped the market. However, record-low interest rates, shifting housing preferences, and government stimulus measures quickly reignited activity, leading to a surge in homebuying and rising prices.
Government Interventions: A Double-Edged Sword

Governments have implemented various interventions to address housing affordability concerns and cool down overheated markets. Measures such as foreign buyer taxes, stress tests for mortgage applicants, and increased housing supply initiatives aim to strike a balance between growth and stability. However, the effectiveness of these interventions remains a subject of debate, with unintended consequences often emerging.
Urbanization and Population Growth: Catalysts for Demand
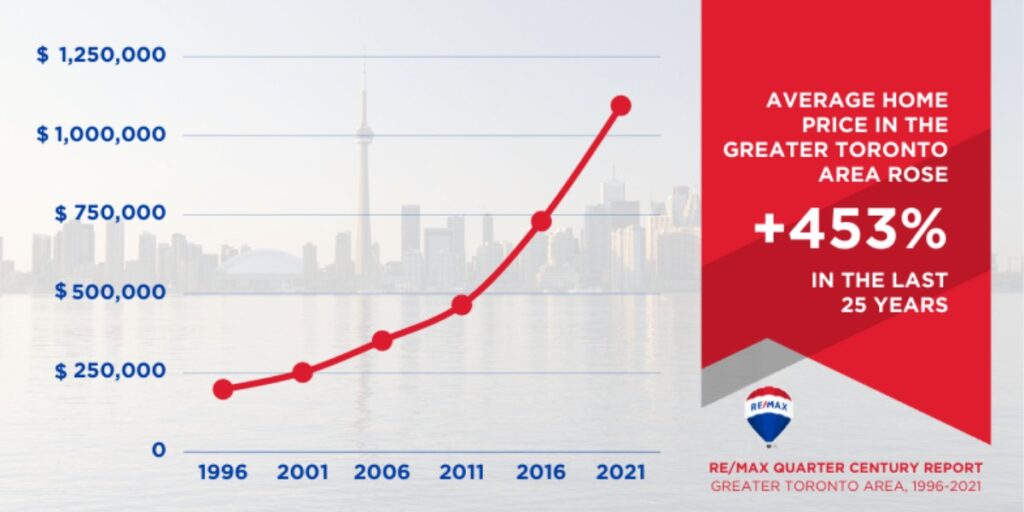
Canada’s urban centers continue to attract a growing influx of residents, driving up demand for housing in cities like Toronto, Vancouver, and Montreal. This trend is fueled by factors such as job opportunities, amenities, and cultural attractions, making urban areas hotbeds for real estate activity.
Low Interest Rates: Fueling the Housing Frenzy

Historically low-interest rates have been a key driver of Canada’s housing frenzy. Cheap borrowing costs incentivize homebuyers to enter the market, increasing purchasing power and driving up prices. While these rates stimulate economic activity, they also contribute to concerns about affordability and financial stability in the long term.
Supply Constraints: A Persistent Challenge

Despite soaring demand, Canada continues to grapple with supply constraints in its housing market. Regulatory hurdles, zoning restrictions, land availability issues, and construction bottlenecks all contribute to a shortage of housing inventory. This imbalance between supply and demand exacerbates affordability pressures and perpetuates the cycle of rising prices.
Changing Consumer Preferences: The Rise of Homeownership
The pandemic has reshaped consumer preferences, with many individuals prioritizing homeownership and space over urban living. Remote work arrangements and a greater emphasis on lifestyle factors have fueled demand for larger homes in suburban and rural areas. This shift in preferences further strains housing supply and affordability, particularly in desirable regions.
The Role of Foreign Investors in Canada’s Housing Market

Foreign investment has been a contentious issue in Canada’s housing market, with concerns about its impact on affordability and market stability. While foreign buyers contribute to demand, particularly in major urban centers, policies aimed at curbing speculative activity have been implemented to mitigate potential risks and ensure fair access to housing for domestic buyers.
Housing Affordability: A Growing Concern

Housing affordability remains a pressing issue across Canada, especially for first-time buyers and low-to-middle-income households. Skyrocketing prices and stagnant wages have widened the affordability gap, making homeownership increasingly elusive for many Canadians. Addressing this challenge requires a multifaceted approach that balances market dynamics with social equity considerations.
Innovative Solutions: Navigating the Housing Dilemma
Addressing Canada’s housing dilemma requires innovative solutions that promote affordability, sustainability, and inclusivity. Collaborative efforts between government, developers, community organizations, and other stakeholders are essential to implementing policies and initiatives that foster a balanced and resilient housing market.
Long-Term Outlook: Can the Demand Sustain?

Looking ahead, the long-term sustainability of Canada’s housing demand remains a subject of speculation. While demographic trends, economic fundamentals, and cultural preferences suggest continued growth, there are risks associated with overheated markets, affordability constraints, and external shocks. Achieving a stable and equitable housing market will require ongoing vigilance and proactive measures.
Balancing Growth and Stability in Canada’s Housing Sector
Canada’s housing market remains a dynamic and complex ecosystem driven by a myriad of factors. Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic and ongoing affordability concerns, demand for housing in Canada shows no signs of waning. Achieving a balance between growth and stability will require collaborative efforts, innovative solutions, and a commitment to addressing the evolving needs of Canadian homeowners and communities.
Click here for more visited Posts!